Genetic algorithms // Form rationalization // Form Finding // Solar facade optimization // From concept to construction, streamlined thanks to digital workflows
Facade consultancy project, AVANCIS GmbH, Computational designer Team leader: Melicia Planchart, Structural engineer: Priedemann Facade Lab, Architecture office: Von Domaros, Client: Stadt Bau Leipzig.
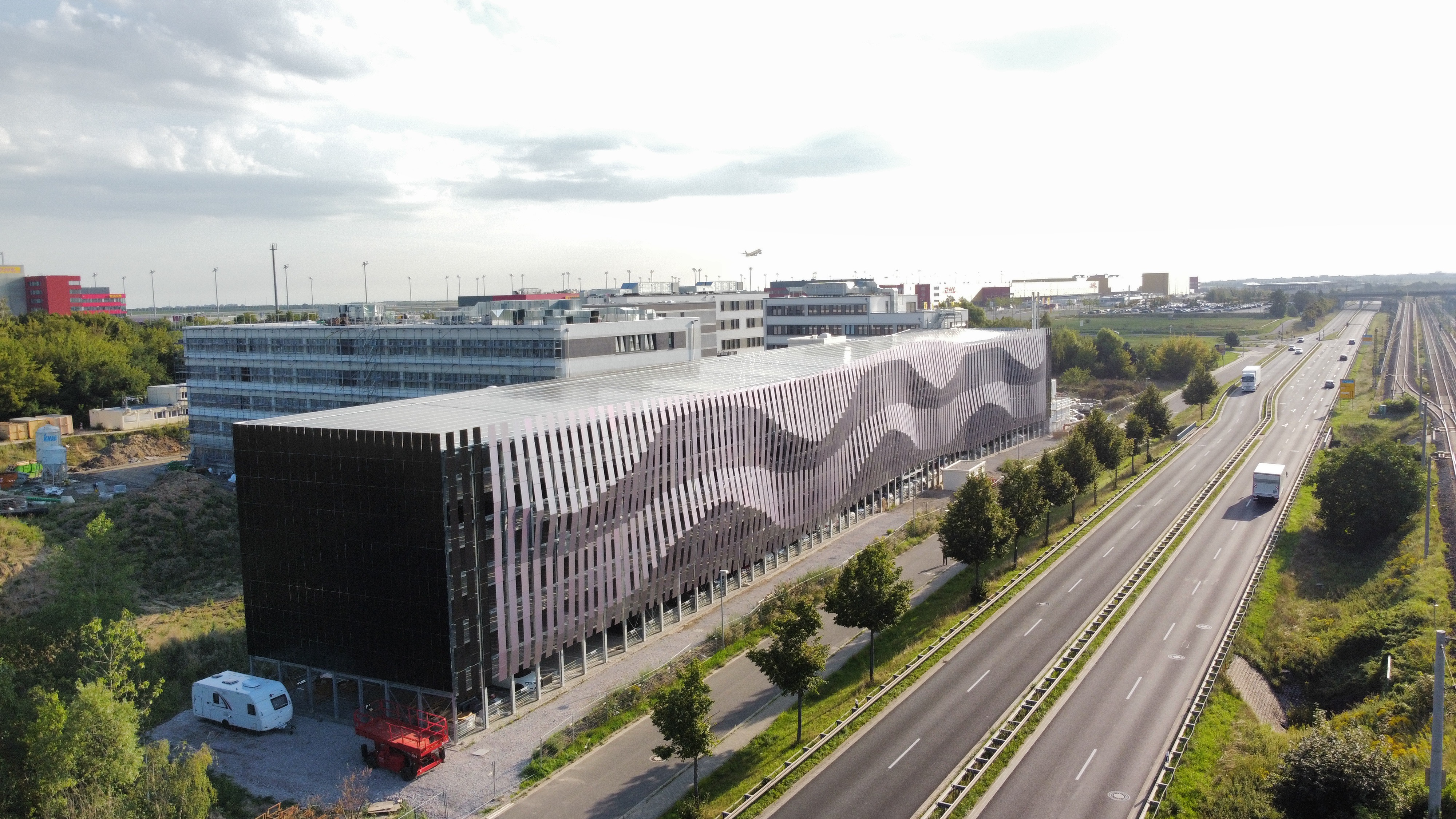
Summary of the DHL Parkhouse Solar Façade Project
The DHL Parkhouse in Leipzig, designed by Von Domaros Architects, features a 2,002-module solar façade optimized using computational design. AVANCIS provided technical consultancy to refine the façade’s shape and reduce costs through shape rationalization and geometric operations, allowing 179 unique substructure frames to be achieved using only 10 base profiles. The final design incorporates an elegant wave pattern, enhancing the color effects of AVANCIS’ solar technology.
By integrating parametric modeling, energy optimization, and predictive analysis, AVANCIS enables informed decision-making for solar façade projects, ensuring an optimal balance between design intent, aesthetics, and efficiency. The DHL Parkhouse project exemplifies how computational tools can bridge the gap between form, function, and stability, setting a benchmark for future Building Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV) applications.
DHL Parking House Solar Façade – Computational Design for BIPV Efficiency
Project Overview
The DHL Parking House in Leipzig features a 2,500 m² Building-Integrated Photovoltaic (BIPV) façade, developed in collaboration with Leipziger Stadtbau and designed by Architektur Von Domaros. AVANCIS provided technical consultancy to optimize the façade for maximum energy yield while preserving its aesthetic integrity. The project highlights how computational design tools streamline the integration of photovoltaics into complex architectural forms.
Computational Design Approach
A digital workflow was implemented to rationalize the freeform façade while ensuring high solar efficiency. Using parametric modeling and genetic algorithms within Rhino and Grasshopper, the team optimized the disposition of Skala solar panels. The methodology focused on three key aspects:
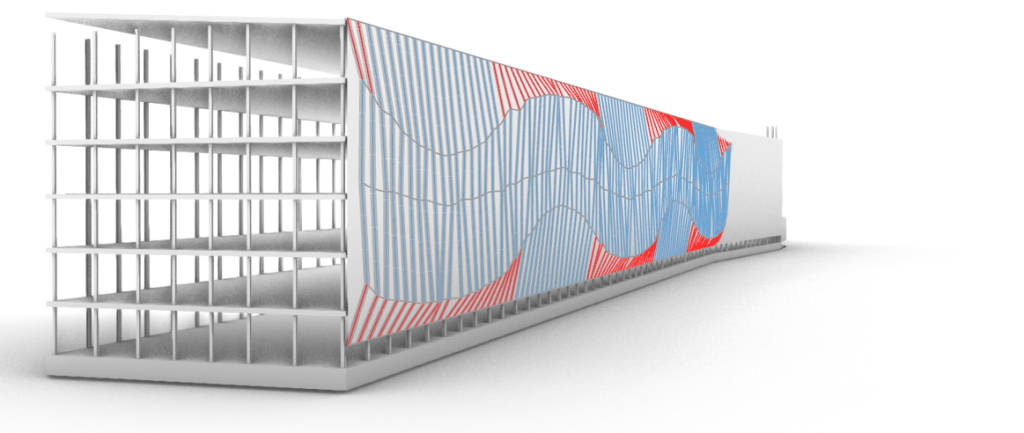
- Form Rationalization: The initial freeform design was refined to align with energy yield goals while maintaining architectural intent.
- Substructure Optimization: A genetic search algorithm minimized the number of custom structural elements, ensuring economic feasibility.
- Panel Layout Optimization: The arrangement of Skala BIPV panels was optimized to maximize standard panel usage and reduce passive elements.
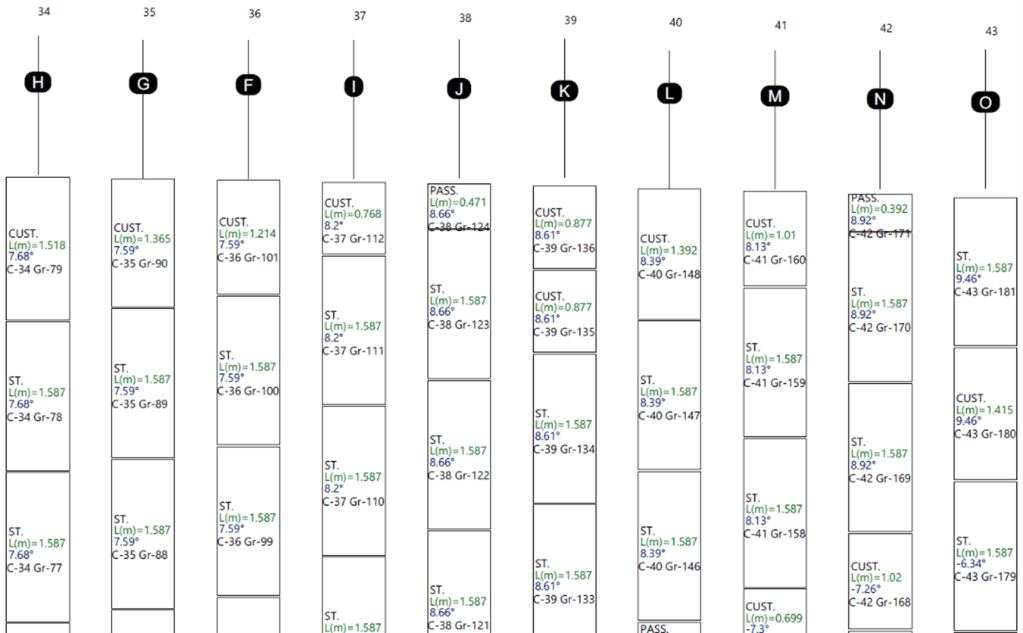
Energy Performance & Yield Simulation
Simulations ensured the optimal orientation and tilt of panels across south, east, and west façades. The design adheres to a key principle: minimizing downward-facing angles beyond 10 degrees to prevent shading losses. The final optimized façade balances energy performance with design flexibility, demonstrating the potential of computational design in BIPV applications.
By leveraging automation and simulation tools, the DHL Parking House BIPV façade achieves a seamless integration of solar technology into a complex architectural form. This project serves as a benchmark for computationally optimized active façades, pushing forward sustainable design in urban infrastructure.



